Cocoa butter is a highly valued natural fat that is derived from cocoa beans and that has a characteristic of quietly melting, creamy texture, and emolliency. It forms the foundation of chocolate manufacturing, a good cocoa butter skin moisturizer, and is used in pharmaceuticals. However, the problem of the price of cocoa butter, the fluctuation of its supply due to climate change and aging plantations, and the rising popularity of alternatives to cocoa butter have caused the problem of substituting cocoa butter to gain more popularity.
These alternatives are meant to mimic the special properties that cocoa butter has, be it in cocoa butter application, cooking, skincare, or pharmaceutical applications, but provide economical and ecologically-friendly alternatives.
Experience Premium Cocoa Butter - Request Your Sample Today!
Substitutes of Cocoa Butter
1.Cocoa Butter Equivalent (CBE)
Shea butter, illip butter, and palm oil are all vegetable fats that are designed to replicate the feel and melting of raw cocoa butter.
- Pros:
- Nearly identical melting points and texture.
- Fully compatible with cocoa butter at high substitution rates.
- Cost-effective and sustainably sourced.
- Cons:
- Supply chain fluctuations (especially palm and shea).
- May slightly alter flavor profile in confectionery.
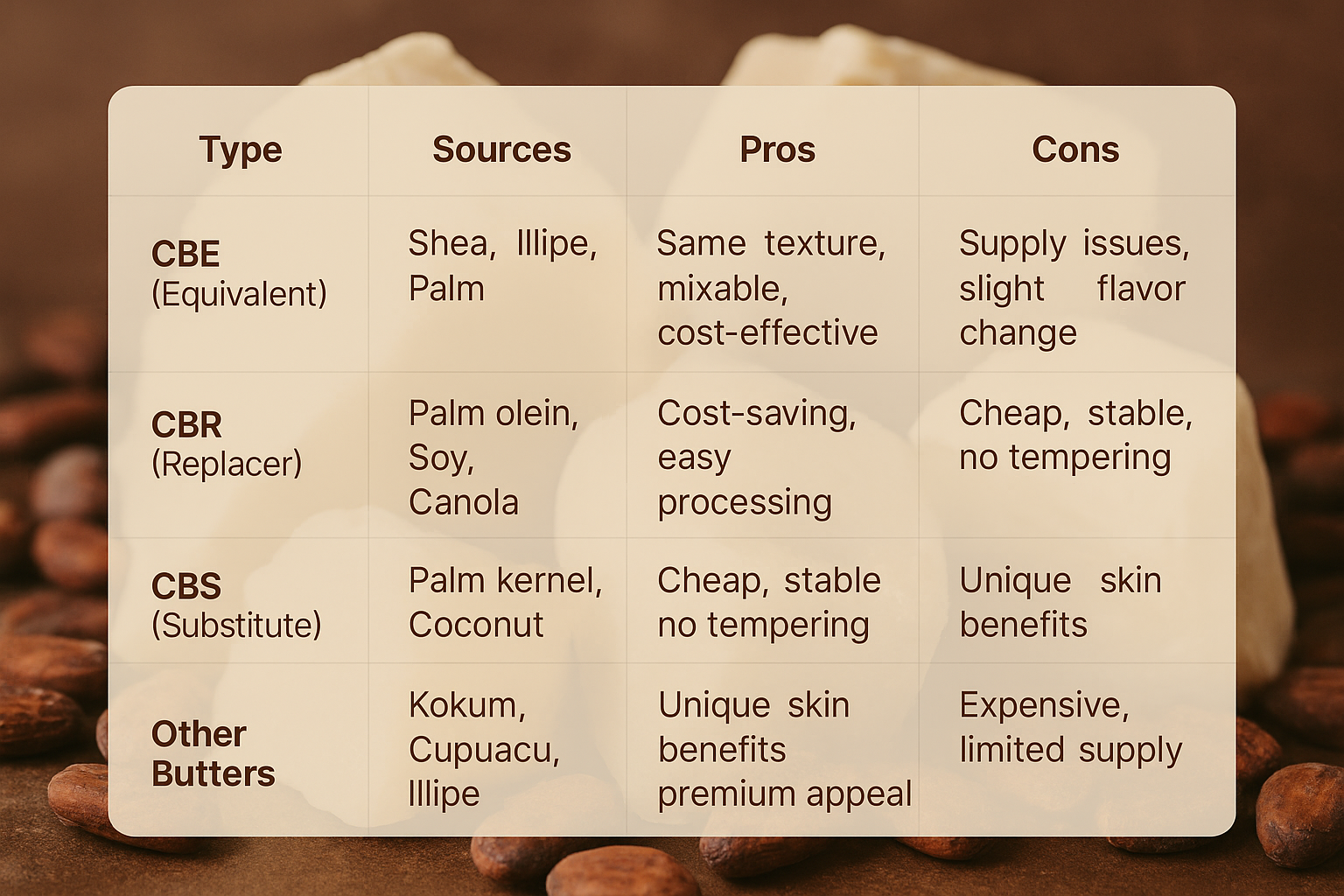
2.Cocoa Butter Replacer (CBR)
Derived from oils like palm olein, soybean, or canola oil, these are designed to partially replace cocoa butter in food and skincare applications.
- Pros:
- Easier processing without complex tempering.
- Enables cost savings while maintaining product quality.
- Cons:
- Limited substitution levels without affecting cocoa butter uses in chocolate and baking.
- Slightly different melting characteristics.
3.Cocoa Butter Substitute (CBS)
Produced from lauric fats such as palm kernel oil or coconut derivatives, CBS is a full replacement for cocoa butter in certain applications.
- Pros:
- Economical and enhances fat crystallization stability.
- No tempering required, simplifying production.
- Cons:
- Alters authentic mouthfeel, making it unsuitable for premium chocolates.
- May not fully replicate cocoa butter benefits for skin when used in personal care.
4. Other Natural Butters
Specialty options such as kokum, cupuacu, and illipe butters are gaining popularity in cosmetics.
- Pros:
- Provides unique moisturizing effects similar to a cocoa butter moisturizer.
- Enhance niche, natural, and premium products.
- Cons:
- Higher cost and limited global supply.
- Require formulation adjustments.
Conclusion
The market demand for cocoa butter substitutes is gradually rising as the industries rely on cost-sustainability, as well as performance. Although cocoa butter is indispensable in chocolate production, bakery, or as a reliable moisturizer in personal care, substitutes are playing a role in ensuring supply availability and expanding its use. Cocoa Butter Equivalents (CBE) is an excellent replica of both raw cocoa butter in confectionery and cocoa butter in cooking, and Cocoa Butter Replacers (CBR) are cheaper and more readily processed. The Cocoa Butter Substitutes (CBS) are popular in the mass-market products, but it does not have the texture and the richness of the good chocolate or the complete benefits of the cocoa butter to the skin. Simultaneously, natural butters like kokum and cupuacu are broadening their chances in the cosmetics sector, with their distinctive moisturizing properties for specialized skincare.
The combination of these solutions makes sure that the versatility of cocoa butter and its numerous applications remain the same in food industries, pharmaceuticals, and beauty industries, even though there are problems with the global supplies.


