

Fluconazole is a triazole antifungal medication used to treat a variety of systemic and superficial fungal infections. It functions by inhibiting the fungal cytochrome P450 enzyme 14α-demethylase, disrupting the conversion of lanosterol to ergosterol, an essential component of the fungal cell membrane. This action renders it effective against infections such as candidiasis, cryptococcosis, and coccidioidomycosis.


Fluconazole is a triazole antifungal medication used to treat a variety of systemic and superficial fungal infections. It functions by inhibiting the fungal cytochrome P450 enzyme 14α-demethylase, disrupting the conversion of lanosterol to ergosterol, an essential component of the fungal cell membrane. This action renders it effective against infections such as candidiasis, cryptococcosis, and coccidioidomycosis.

.3d8f8f41.svg)
Pharmaceutical
.3556d45a.svg)

Pharmaceutical Actives & Precursors


Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
.7767eb0f.png)

Chemical Properties & Specifications
Used as an active ingredient in antifungal medications for treating infections like candidiasis, cryptococcosis, and other systemic fungal infections.
Employed in studies focusing on antifungal therapies and fungal cell membrane synthesis.
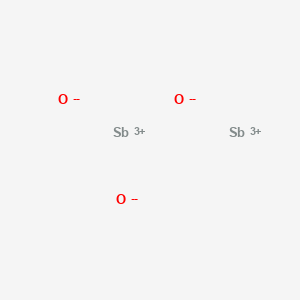
CAS No. : 1309-64-4
Category : Synergists & Smoke Suppressants
Sub-Category : Antimony-based synergists
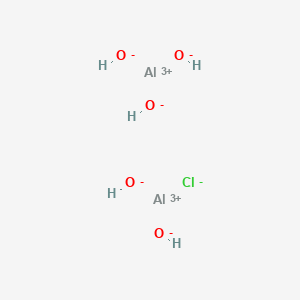
CAS No. : 1327-41-9
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : Metal-Based Coagulants
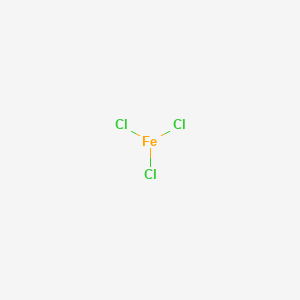
CAS No. : 7705-08-0
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : Metal-Based Coagulants
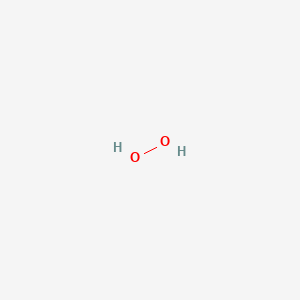
CAS No. : 7722-84-1
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : Peroxides & Oxidizing Agents

CAS No. : 1309-48-4
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)

CAS No. : 13463-67-7
Category : Pigments & Colorants
Sub-Category : Inorganic Pigments

CAS No. : 13463-67-7
Category : Pigments & Colorants
Sub-Category : Inorganic Pigments

CAS No. : 13463-67-7
Category : Pigments & Colorants
Sub-Category : Inorganic Pigments
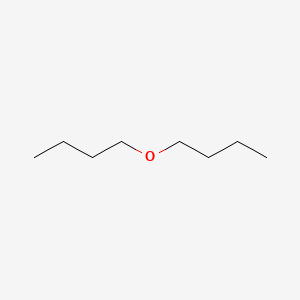
CAS No. : 142-96-1
Category : Solvents & Carriers
Sub-Category : Ethers & Ether-Based Solvents
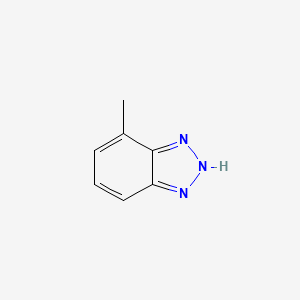
CAS No. : 29385-43-1
Category : Specialty Polymers & Additives
Sub-Category : Corrosion Inhibitor Additives
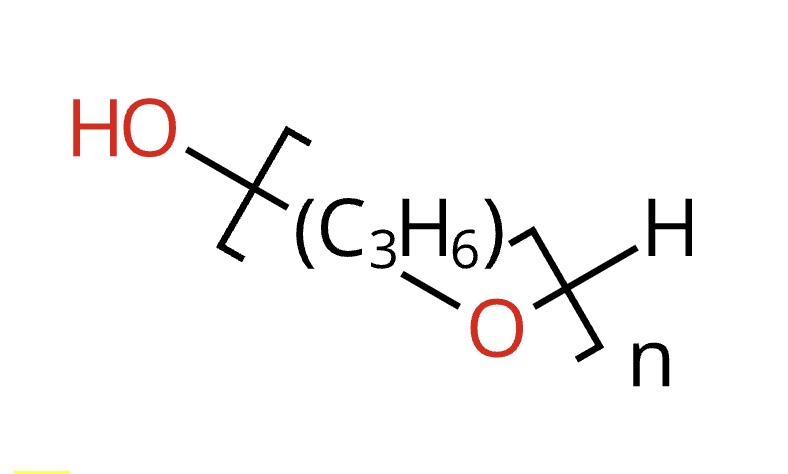
CAS No. : 25322-69-4
Category : Specialty Polymers & Additives
Sub-Category : Polyether Polyols
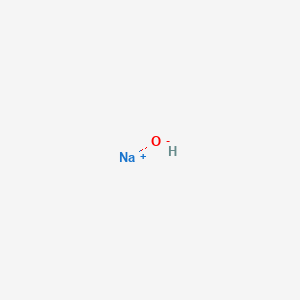
CAS No. : 1310-73-2
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : Alkalis & Bases
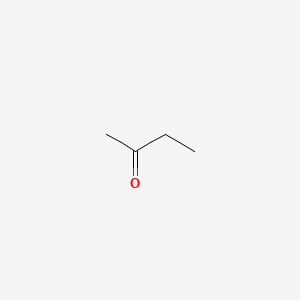
CAS No. : 78-93-3
Category : Base Chemicals & Intermediates
Sub-Category : Ketones & Solvents
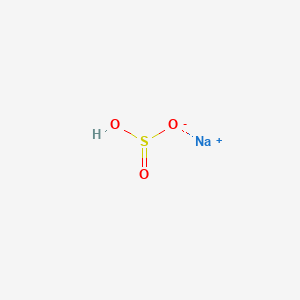
CAS No. : 7631-90-5
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : Sulfur-Based Compounds
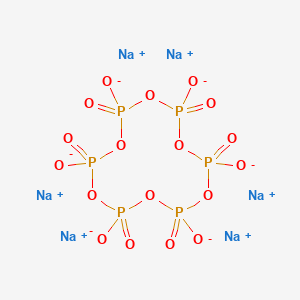
CAS No. : 10124-56-8
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : Phosphate Compounds
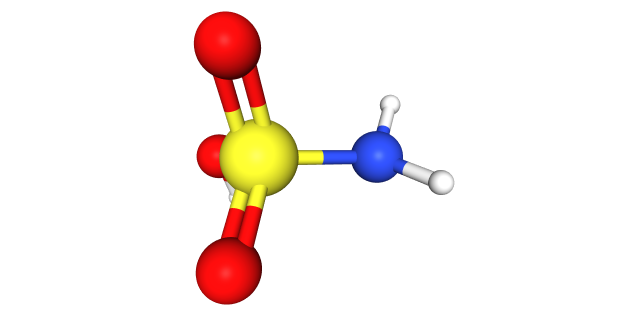
CAS No. : 5329-14-6
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : Acid Derivatives
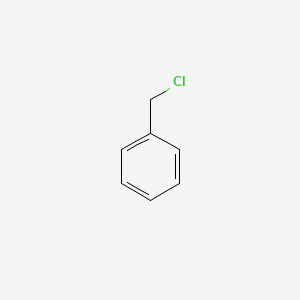
CAS No. : 100-44-7
Category : Organic Intermediates
Sub-Category : Chlorinated Aromatic Compounds
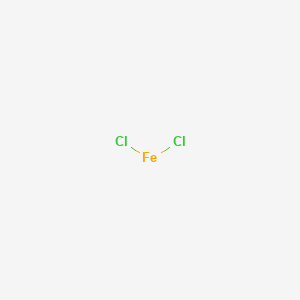
CAS No. : 7758-94-3
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : Metal Halides
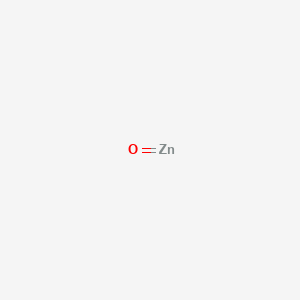
CAS No. : 1314-13-2
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : N/A
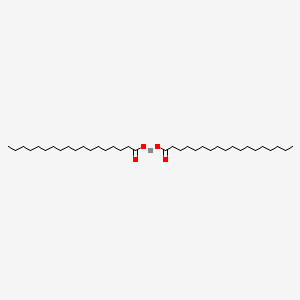
CAS No. : 136-53-8
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : Metal Carboxylates
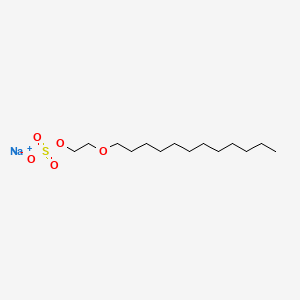
CAS No. : 9004-82-4
Category : Surfactants
Sub-Category : Anionic (Ether sulfates)
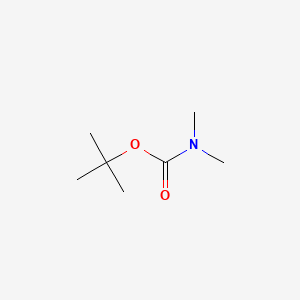
CAS No. : 61788-93-0
Category : Surfactants & Emulsifiers
Sub-Category : Fatty Amines
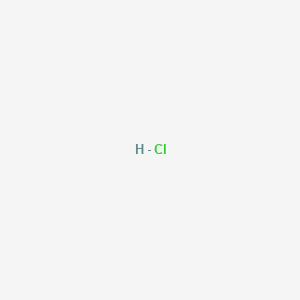
CAS No. : 7647-01-0
Category : Inorganic Acids
Sub-Category : Mineral Acids
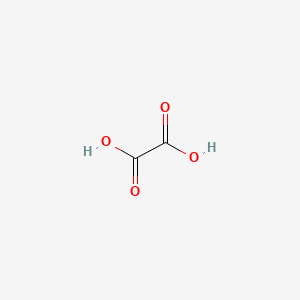
CAS No. : 144-62-7
Category : Organic Acid Derivatives
Sub-Category : Dicarboxylic Acids
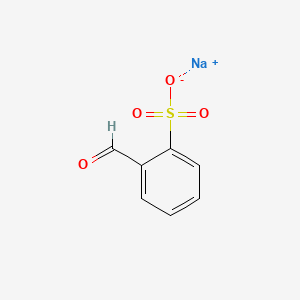
CAS No. : 17465-11-3
Category : Organic Intermediates
Sub-Category : Aromatic Sulfonates

CAS No. : 7704-34-9
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : Sulfur & Derivatives
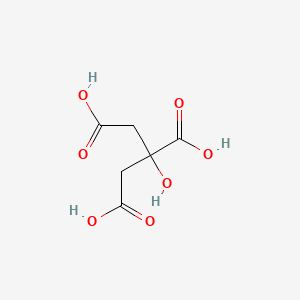
CAS No. : 77-92-9
Category : Food Ingredients
Sub-Category : Flavor Enhancers

CAS No. : 7631-90-5
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : Sulfur-Based Compounds

CAS No. : 10124-56-8
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : Phosphate Compounds
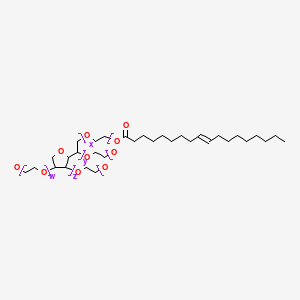
CAS No. : 9005-65-6
Category : Surfactants & Emulsifiers
Sub-Category : N/A
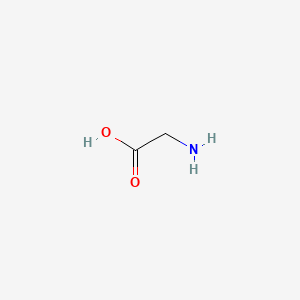
CAS No. : 56-40-6
Category : Nutraceutical Ingredients
Sub-Category : Amino Acids & Proteins

CAS No. : 8002-31-1
Category : Food Ingredients
Sub-Category : Cocoa & Chocolate Derivatives

CAS No. : 84649-99-0
Category : Food Ingredients
Sub-Category : Cocoa & Chocolate Derivatives

CAS No. : 84649-99-0
Category : Food Ingredients
Sub-Category : Cocoa & Chocolate Derivatives

CAS No. : 84649-99-0
Category : Food Ingredients
Sub-Category : Cocoa & Chocolate Derivatives
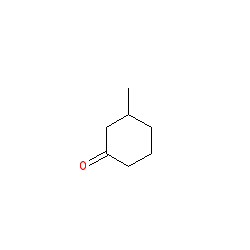
CAS No. : 36306-87-3
Category : Fragrance Ingredients
Sub-Category : Ionones & Ketones
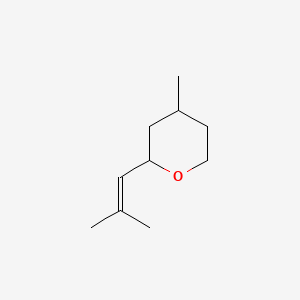
CAS No. : 16409-43-1
Category : Fragrance Ingredients
Sub-Category : Aroma Compounds
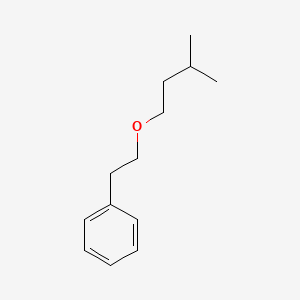
CAS No. : 56011-02-0
Category : Fragrance Ingredients
Sub-Category : Aliphatic Aromatic Ethers
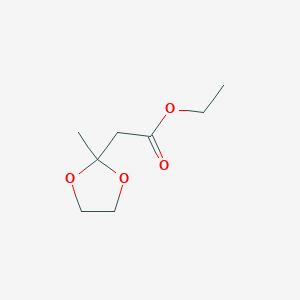
CAS No. : 6413-10-1
Category : Fragrance Ingredients
Sub-Category : Ketal Fruit Esters
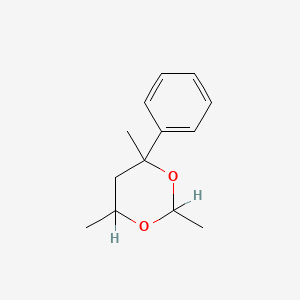
CAS No. : 5182-36-5
Category : Fragrance Ingredients
Sub-Category : Aroma Chemicals
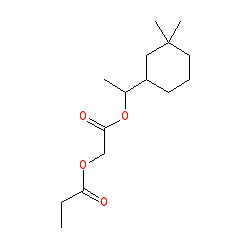
CAS No. : 236391-76-7
Category : Fragrance Ingredients
Sub-Category : Polycyclic Synthetic Musks

CAS No. : 236391-76-7
Category : Fragrance Ingredients
Sub-Category : Polycyclic Synthetic Musks
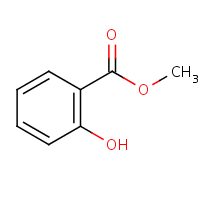
CAS No. : 119-36-8
Category : Fragrance Ingredients
Sub-Category : Aromatic Esters