

N,N'-Carbonyl diimidazole (CDI) is an organic reagent primarily used in peptide synthesis, protein modification, and pharmaceutical research. It serves as a coupling reagent in peptide bond formation, promoting the reaction between amines and carboxylic acids. CDI is widely used in chemical manufacturing, particularly in the creation of bioconjugates, owing to its efficiency in activating carboxyl groups. It also plays a crucial role in the synthesis of nucleic acid derivatives and other complex organic molecules


N,N'-Carbonyl diimidazole (CDI) is an organic reagent primarily used in peptide synthesis, protein modification, and pharmaceutical research. It serves as a coupling reagent in peptide bond formation, promoting the reaction between amines and carboxylic acids. CDI is widely used in chemical manufacturing, particularly in the creation of bioconjugates, owing to its efficiency in activating carboxyl groups. It also plays a crucial role in the synthesis of nucleic acid derivatives and other complex organic molecules

.3d8f8f41.svg)
Pharmaceutical
.3556d45a.svg)

Pharmaceutical Actives & Precursors


Intermediates & Precursors
.7767eb0f.png)

Chemical Properties & Specifications
Used in peptide synthesis, especially for the coupling of amino acids in the formation of peptides and proteins.
Serves as a reagent in the synthesis of bioconjugates and nucleic acid derivatives.
Utilized in organic synthesis, particularly in modifying biomolecules for various chemical applications.
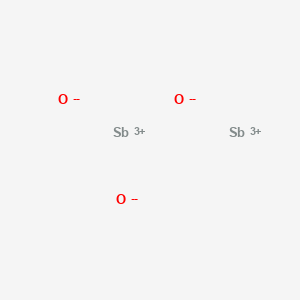
CAS No. : 1309-64-4
Category : Synergists & Smoke Suppressants
Sub-Category : Antimony-based synergists
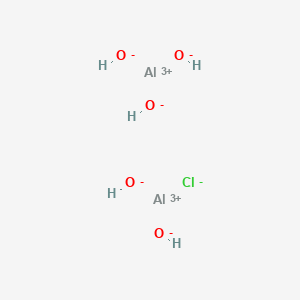
CAS No. : 1327-41-9
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : Metal-Based Coagulants
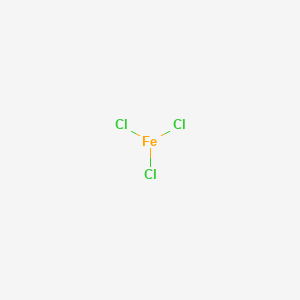
CAS No. : 7705-08-0
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : Metal-Based Coagulants
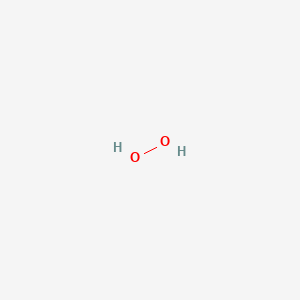
CAS No. : 7722-84-1
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : Peroxides & Oxidizing Agents

CAS No. : 1309-48-4
Category : Pharmaceutical Actives & Precursors
Sub-Category : Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)

CAS No. : 13463-67-7
Category : Pigments & Colorants
Sub-Category : Inorganic Pigments

CAS No. : 13463-67-7
Category : Pigments & Colorants
Sub-Category : Inorganic Pigments

CAS No. : 13463-67-7
Category : Pigments & Colorants
Sub-Category : Inorganic Pigments
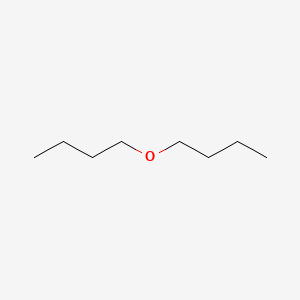
CAS No. : 142-96-1
Category : Solvents & Carriers
Sub-Category : Ethers & Ether-Based Solvents
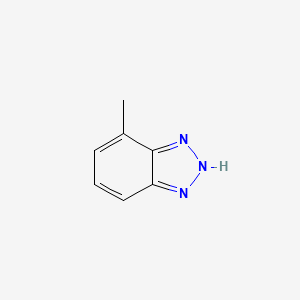
CAS No. : 29385-43-1
Category : Specialty Polymers & Additives
Sub-Category : Corrosion Inhibitor Additives
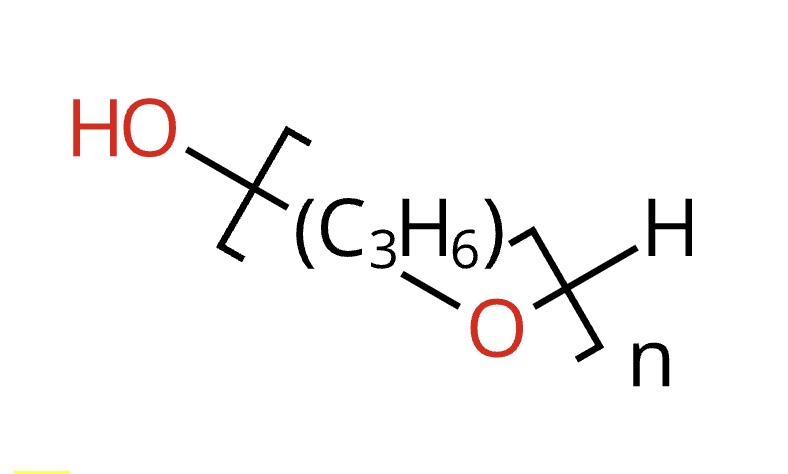
CAS No. : 25322-69-4
Category : Specialty Polymers & Additives
Sub-Category : Polyether Polyols
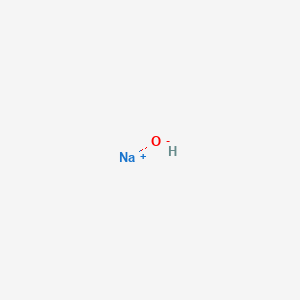
CAS No. : 1310-73-2
Category : Food Ingredients
Sub-Category : Acidulants & Acidity Regulators
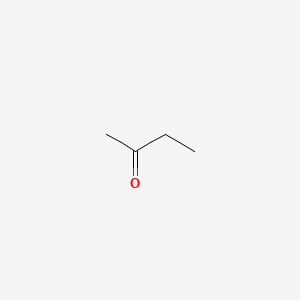
CAS No. : 78-93-3
Category : Base Chemicals & Intermediates
Sub-Category : Ketones & Solvents
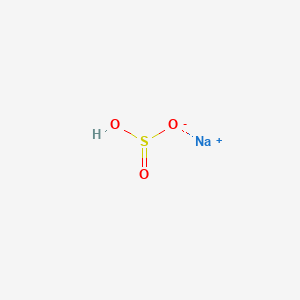
CAS No. : 7631-90-5
Category : Food Ingredients
Sub-Category : Sulfur-Based Compounds
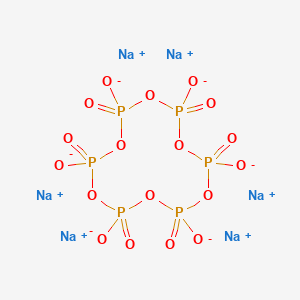
CAS No. : 10124-56-8
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : Phosphate Compounds
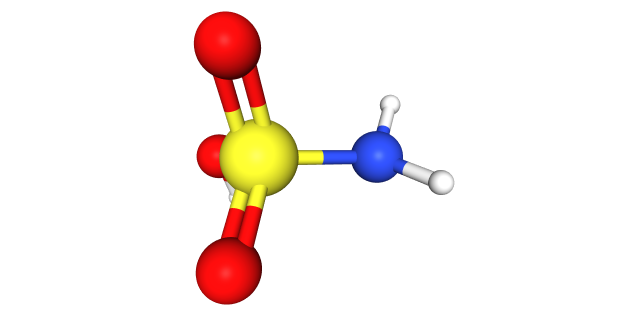
CAS No. : 5329-14-6
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : Acid Derivatives
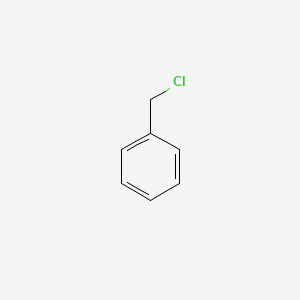
CAS No. : 100-44-7
Category : Organic Intermediates
Sub-Category : Chlorinated Aromatic Compounds
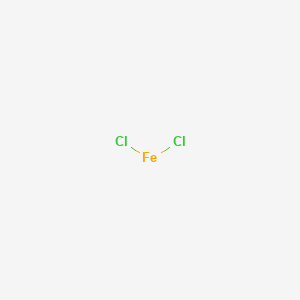
CAS No. : 7758-94-3
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : N/A
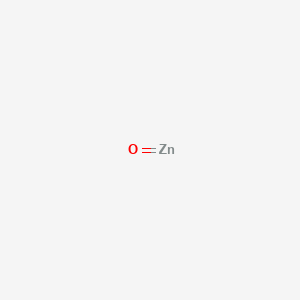
CAS No. : 1314-13-2
Category : Plant Health, Nutrients & Soil Management
Sub-Category : Zinc-Based Functional Additives
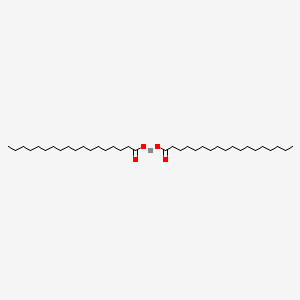
CAS No. : 136-53-8
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : Metal Carboxylates
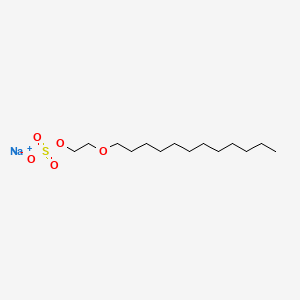
CAS No. : 9004-82-4
Category : Surfactants
Sub-Category : Anionic (Ether sulfates)
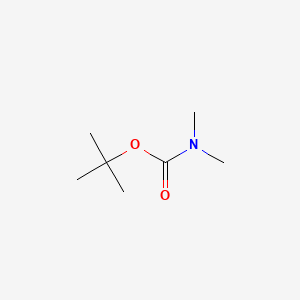
CAS No. : 61788-93-0
Category : Surfactants & Emulsifiers
Sub-Category : Fatty Amines
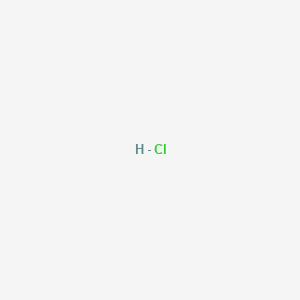
CAS No. : 7647-01-0
Category : Inorganic Acids
Sub-Category : Mineral Acids
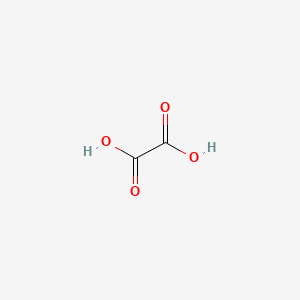
CAS No. : 144-62-7
Category : Organic Acid Derivatives
Sub-Category : Dicarboxylic Acids

CAS No. : 7704-34-9
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : Sulfur & Derivatives
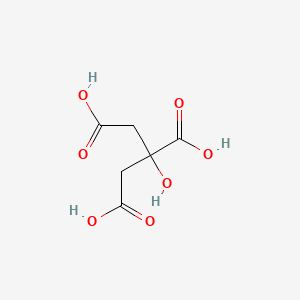
CAS No. : 77-92-9
Category : Food Ingredients
Sub-Category : Flavor Enhancers
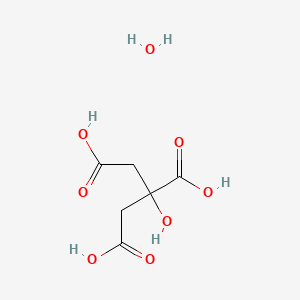
CAS No. : 5949-29-1
Category : Food Ingredients
Sub-Category : Flavor Enhancers

CAS No. : 7631-90-5
Category : Food Ingredients
Sub-Category : Sulfur-Based Compounds

CAS No. : 10124-56-8
Category : Inorganic Chemicals
Sub-Category : Phosphate Compounds
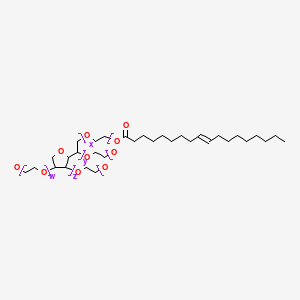
CAS No. : 9005-65-6
Category : Surfactants & Emulsifiers
Sub-Category : Functional Emulsifiers
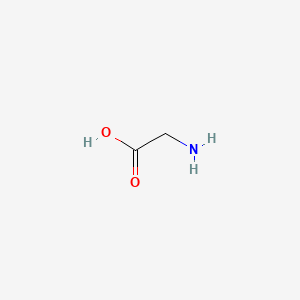
CAS No. : 56-40-6
Category : Nutraceutical Ingredients
Sub-Category : Amino Acids & Proteins

CAS No. : 8002-31-1
Category : Food Ingredients
Sub-Category : Cocoa & Chocolate Derivatives
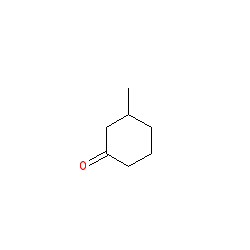
CAS No. : 36306-87-3
Category : Fragrance Ingredients
Sub-Category : Ionones & Ketones
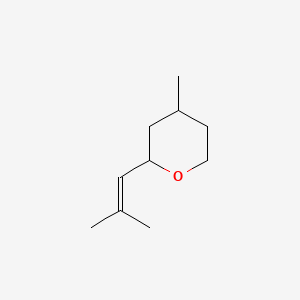
CAS No. : 16409-43-1
Category : Fragrance Ingredients
Sub-Category : Cyclic Alcohols & Ethers